Exploring Faux Naïf: How Contemporary Artists Adopt A Naïve art Aesthetic
Naive art and faux-naif art employ a simplistic, childlike aesthetic that appears unschooled and unstudied. Though the two styles share similarities, they have distinct origins and contexts in the art world. This article will define naive and faux-naif art, trace their emergence and acceptance in the fine art world, describe their key characteristics, and highlight major artists associated with each style.
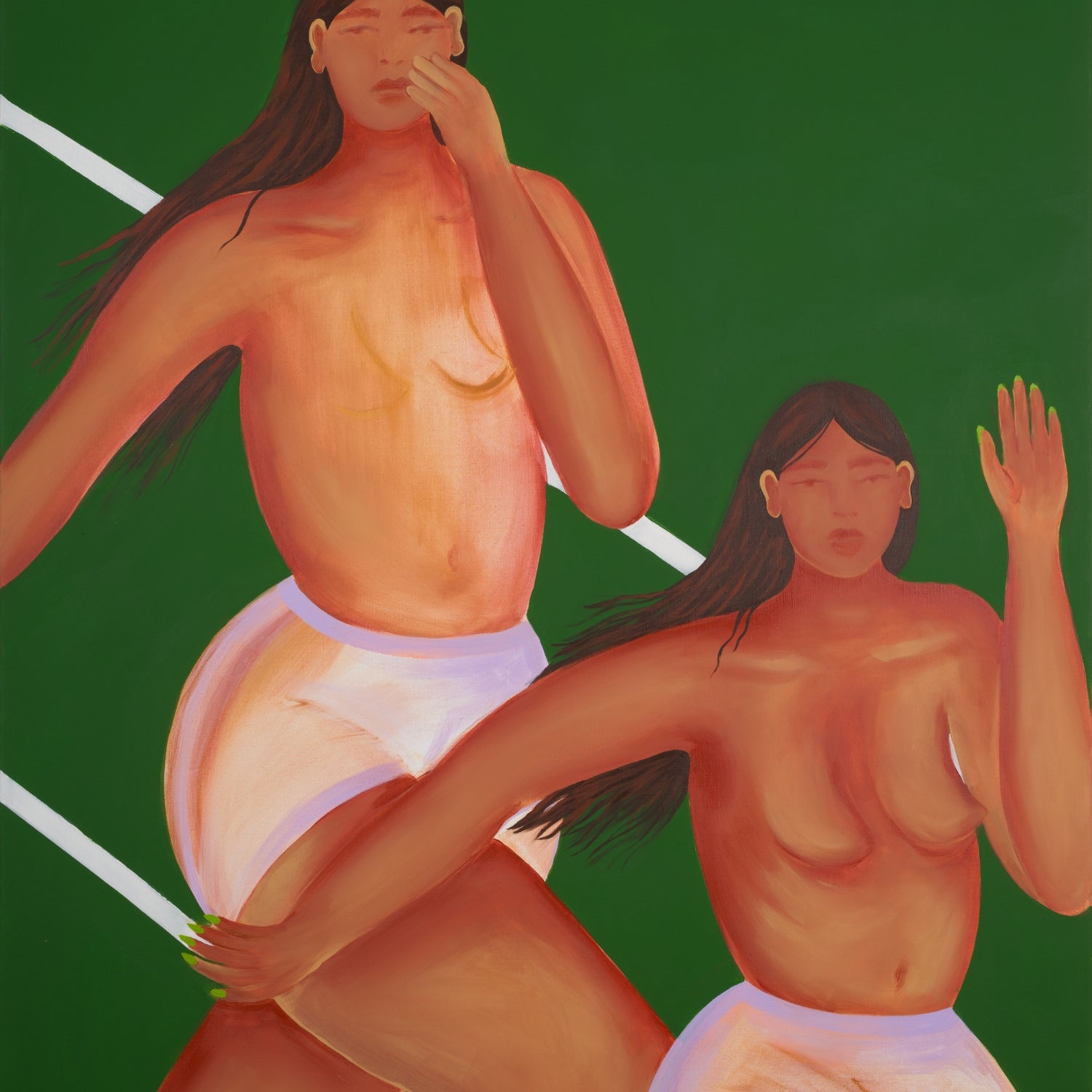
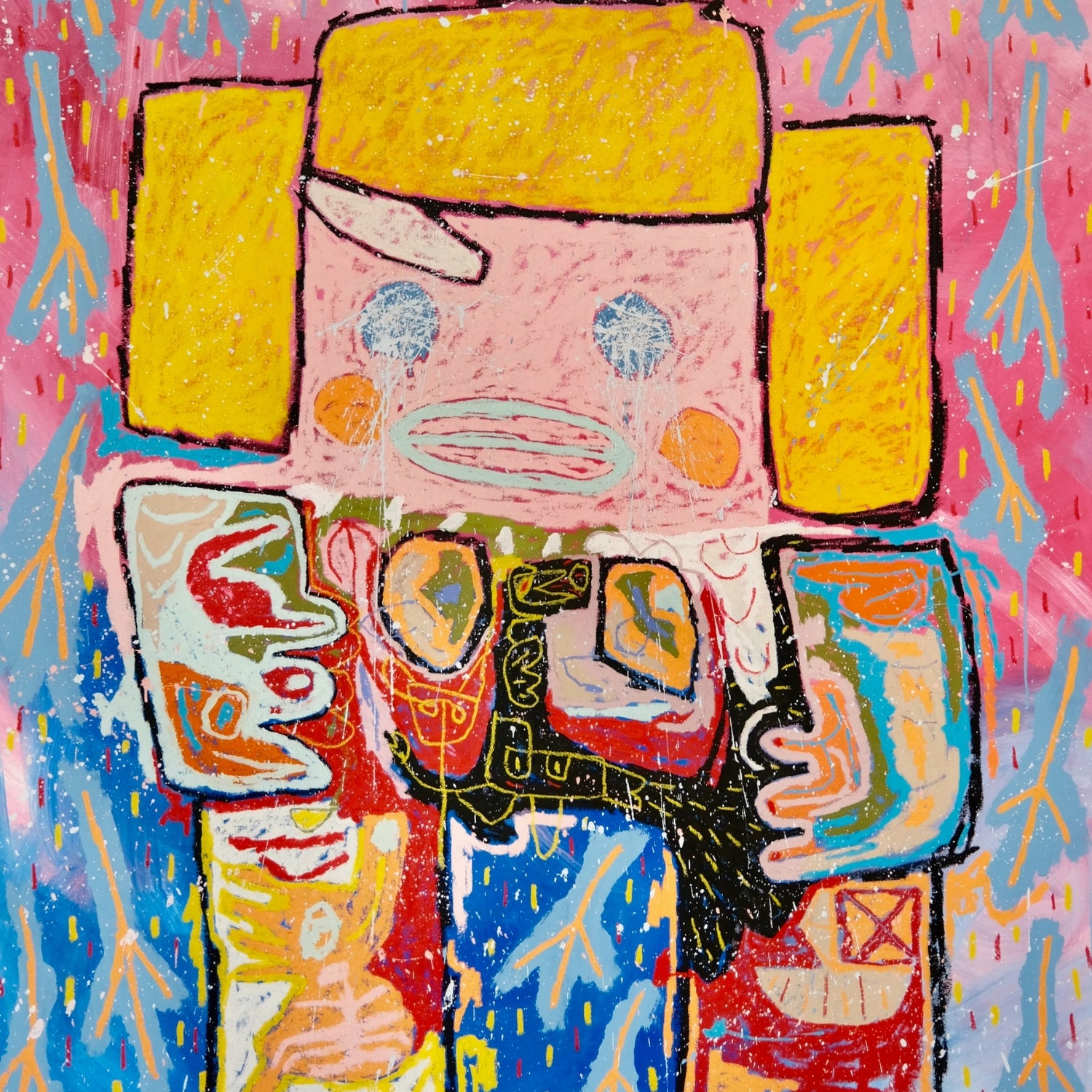
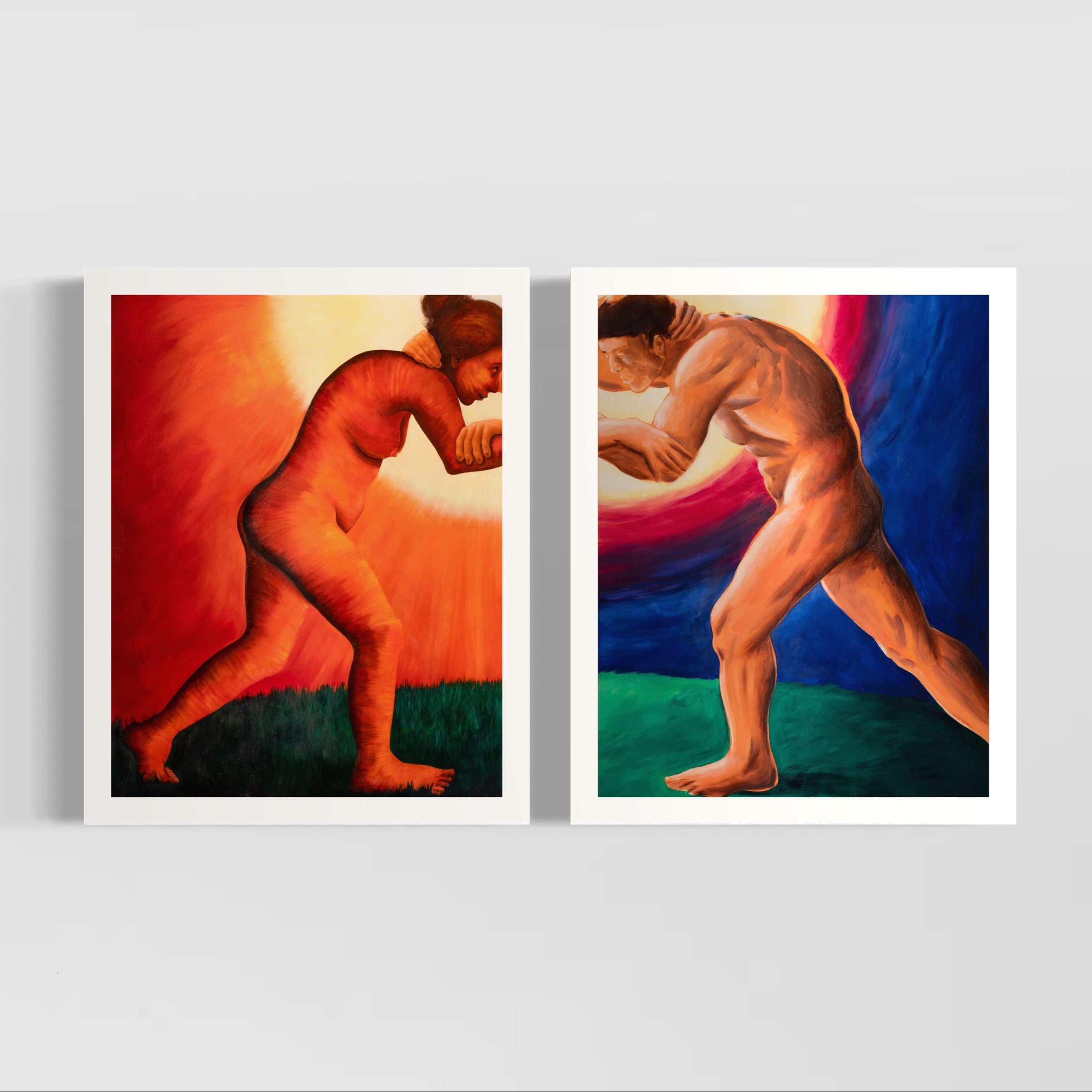
Adam Handler, Pajama Girl ghost abduction, 2023
What is Naive Art?
Naive art is created by self-taught artists who lack formal training in perspective, composition, color theory and other elements of representational art. It displays a frank, intuitive approach to subject matter, with awkward perspectives, vivid colors, and flattened space. Figures and objects are depicted in a direct, childlike manner.
The term was first used in the late 19th century to describe the work of artists like Henri Rousseau, who had no academic art education but created imaginative, exotic scenes drawn from nature and his own dreams.
In the early 20th century, the childlike qualities of naive art were appreciated by modernists like Picasso as an antidote to academic realism. The Surrealists were also drawn to the strange dreamscapes of artists like Rousseau.
Over time, naive art earned recognition as a valid style all its own, with acclaimed museums and galleries dedicated to showcasing it. It continues to inspire contemporary artists looking to tap into raw creativity.
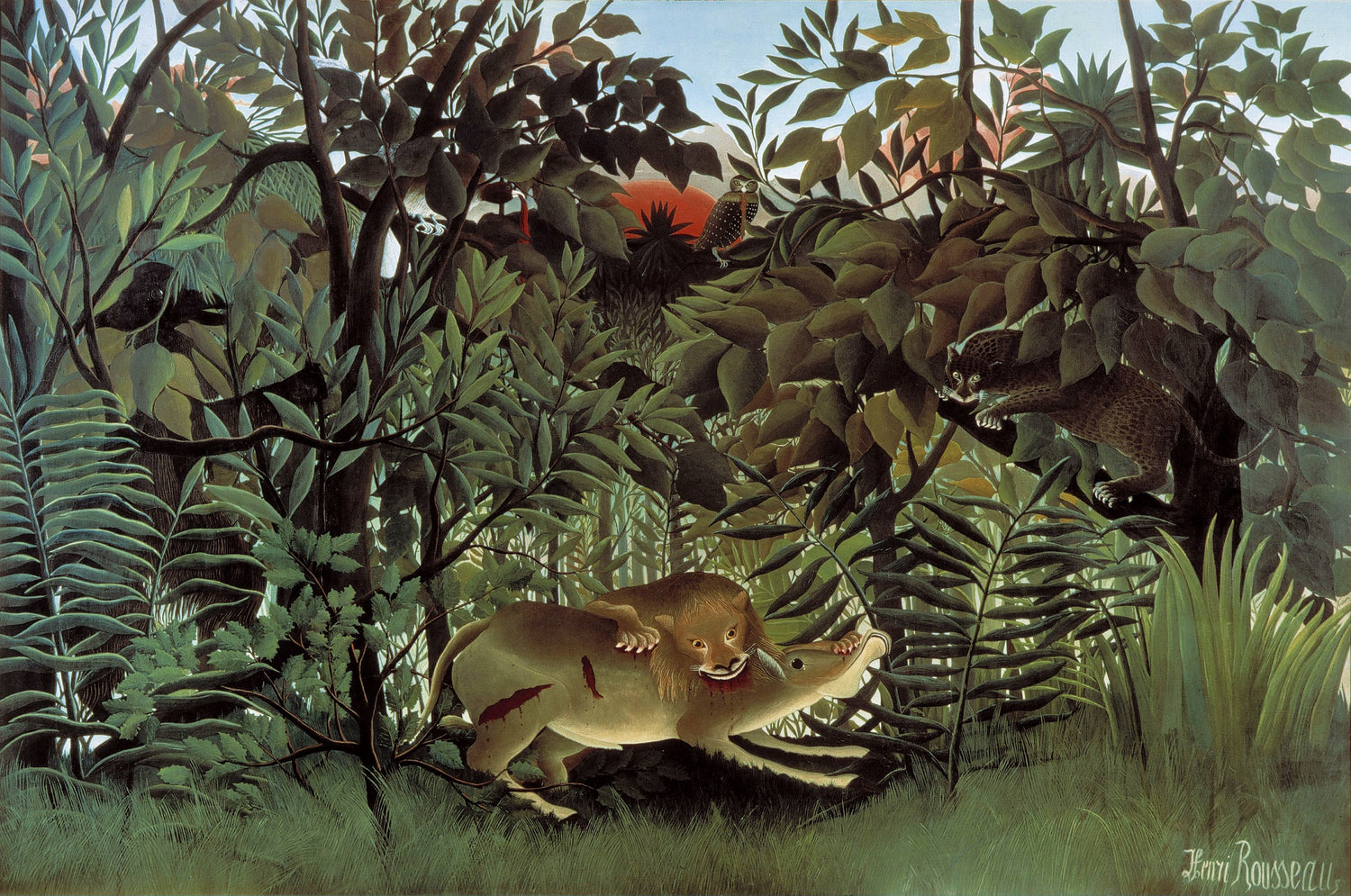
The Hungry Lion Attacking An Antelope, Henri Rousseau, 1898-1905
What is faux naïf Art?
Whereas naive art is unschooled and guileless, faux-naif or "false naive" art is a 20th century phenomenon in which academically trained fine artists intentionally emulate the naive style.
Faux-naif art emerged as modern artists sought to break with realism and recover a more primal, direct means of expression. They imitated the flat perspectives, frank colors and simple forms of naive works, but their efforts were more self-conscious and contrived.
Key faux-naif artists include Paul Klee, Jean Dubuffet, Alfred Manessier, Bernard Buffet and the CoBrA group. Some contemporary artists working in a faux-naive vein include Tal R and Jules de Balincourt.
Critics argue whether faux naive art captures the authentic spirit of outsider art or merely appropriates it for novelty. But it continues to attract those who see naive qualities as liberating traditional technique.
JOACHIM LAMBRECHTS, New York City, 2023
Characteristics of Naive Art
- Frankness and intimacy - Naive art has an unabashed, confessional flavor. Subjects are portrayed in an unidealized, matter-of-fact way.
- Flat, awkward perspectives - The ordinary rules of perspective are ignored, with no horizon line and little sense of depth. Objects appear stacked up almost randomly.
- Bright, arbitrary colors - Colors tend to be pure and surreal, with no attempt at naturalism. Hues appear unmixed and vivid.
- Heavy outlines - Figures and objects are outlined thickly in dark colors. Details are rendered crudely.
- Whimsical, imaginative themes - Subject matter draws from religion, fantasy, memory, and ideals of innocence. Landscapes combine observed reality with dreamed settings.
- Simplified forms - Compositions have a spare, elegant rhythm. Backgrounds lack detail, putting all focus on the central motif.
- Raw, intuitive mark-making - Paint is applied expressively, with little blending or correction. Brushwork feels spontaneous and improvised.
Key Naive Artists and Artworks
Henri Rousseau
- French post-Impressionist painter celebrated for his lush jungle scenes. His work mixed observed botanical details with imagined settings.
- Famous works: The Dream (1910), The Hungry Lion Throws Itself on the Antelope (1905).
Séraphine Louis
- French artist who created brilliantly colored, flat renderings of flowers. Lived in poverty but gained renown after her death.
- Famous works: Flowers (1930), Leaves and Flowers (1930).
Grandma Moses
- American folk artist who started painting at 78. She captured American rural life in vivid, nostalgic images.
- Famous works: Out for Christmas Trees (1948), Fourth of July (1951).
Themes and Subjects
Naive artists draw from religion, fantasy, memory, and idealized views of childhood and nature. Some common motifs include:
- Landscapes / cityscapes - painted from memory, mixing real places with imagined elements. May reflect nostalgia for hometowns or villages.
- Still lifes - of ordinary household objects like flowers, fruit, and kitchenware. Often flat and brightly colored.
- Religious figures - such as the Madonna, angels and saints. Portrayed in a simple, reverent manner.
- Personal memories - sentimental scenes from the artist's past, such as village festivals, weddings, funerals.
- Dreams and fantasies - surreal scenes expressing hopes, fears, desires or escapist dreams. Jungles were a frequent motif.
- Children - painted as pure, innocent figures removed from adult rules and corruption.
- Animals - portrayed in harmony with humans, or symbolizing certain virtues.
Faux-naif artists adopt similar motifs, filtering them through awareness of art historical styles and concepts. There is often subtle subversion or dark undertones absent from genuine naive works.
Contemporary Naive Artists We Exhibit
Adam Handler
Emerging New York artist Adam Handler discovered his passion studying art history in college. His faux-naif paintings in vibrant colors aim to evoke emotions rather than contemplation. Spontaneity fuels his creative process, with delightful surprises emerging. His ghost paintings and figurative elements contribute a distinctive naive style.
Joachim Lambrechts
Renowned Belgian urban artist Joachim Lambrechts began as a street artist in Antwerp before focusing on canvas painting. In contrast to his planned murals, his studio works are spontaneous, channeling a sense of urgency and innocence. Their freer approach brings a naive quality to his expressive paintings.
Why Does Naive Art Endure?
What explains naive art’s lasting appeal? For us, key factors include:
- Authenticity - It's seen as pure visionary art, uncorrupted by formal training.
- Nostalgia - The style evokes childhood memories and fading traditions.
- Escapism - Its joyful fantasies counter modern disillusionment.
- Creativity - Its disregard for realism and lush colors inspire.
- Inspirational - The passion and resourcefulness of outsider artists uplifts.
Most of all, naive art remains powerful through its rare emotional honesty and intimacy. Devoid of artistic pretensions, it speaks straight from the heart.
The Allure of Naiveté
At Cohle Gallery, naive and faux-naif styles capture imaginative freedom detached from strict mimesis. Both allow artists to break from realism through a guileless, unstudied aesthetic.
Yet as we've seen, naive art derives from sincere outsider expression, while faux-naif reinterprets it knowingly. We appreciate merits in both, though debates around intent persist.
Ultimately, the magnetic appeal of naive art is undeniable to us. Its color, intimacy and childlike candor provide an antidote to postmodern irony and cynicism. It stands outside time, evoking wonder through innocent eyes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key differences between naive art and faux-naif art?
The main difference is that naive art is created by untrained artists outside the mainstream art world, while faux-naif or "false naive" art is created by academically trained fine artists emulating the naive aesthetic.
Who were some of the earliest naive artists?
Some of the earliest influential naive artists include Henri Rousseau, Alfred Wallis, André Bauchant, Séraphine Louis, and Grandma Moses.
What contemporary artists work in a naive or faux-naive style?
Some contemporary artists exploring naive or faux-naive styles include Jules de Balincourt, Tal R, Nellie Mae Rowe, Lee Godie, and Janko Brašić.
How has the art world's perception of naive art evolved over time?
Once dismissed as amateurish, naive art gained appreciation in the early 20th century as modernists celebrated its authenticity. It is now recognized as a valid, influential style with acclaimed museums and galleries devoted to it.
What are some common themes and subjects in naive art?
Common naive art themes include religion, fantasy, memory, childhood, nostalgic landscapes, still lifes, and personal recollections rendered in a frank, intuitive way.